
A period cost is charged to expense on the income statement as soon as it is incurred. Reporting period costs cash flow are based on the revenue for which they are incurred and the accrual for a specific accounting period. These expenses are charged to the statement of profit & loss and are not directly related to production. Period costs reduced net income when they are expensed on the income statement. Period costs take from the revenue of a company during that accounting period and thus will have an impact on the net income for that period.
- Also, fixed and variable costs may be calculated differently at different phases in a business’s life cycle or accounting year.
- Period expenses appear on the income statement with an appropriate caption for the item, which acts as a disclosure, in the period when the cost is incurred or recognized.
- For instance, office rent is recorded as an expense in the month it is paid, irrespective of the sales activities of that month.
- For instance, a spike in rental expenses due to market changes would necessitate a reevaluation of pricing to ensure that the increased costs do not erode profit margins.
- This comprehensive budgeting ensures that all aspects of the company’s financial obligations are anticipated and accounted for, allowing for a more robust financial plan.
What Effect Does Period Cost Have on the Income Statement?
It’s like finding the right balance to make good products and keep the entire business in good shape. Product and period costs take part in the financial story, influencing the bottom line and revealing the business’s financial health. When you look at a business’s income statement or a balance sheet, product and period costs show up there, influencing different parts of these financial statements. Understanding period costs helps assess the day-to-day financial health of a business. And while product costs focus on the creation of goods or services, period costs represent the broader expenses period costs formula necessary to sustain the business’s overall operations and facilitate growth. Unlike product costs, period costs don’t depend on the production volume.
The timing of product costs

This timing is crucial for accurately determining the total cost of producing each unit. As a general rule, costs are recognized as expenses on the income statement in the period that the benefit was derived from the cost. So if you pay for two years of liability insurance, it wouldn’t be good to claim all of that expense in the period the bill was paid.
Is Converting Your Personal Vehicle for Business Use a Good Idea?
The main characteristic of these costs is that they are incurred over a period of time (during the accounting period). Unlike period expenses, operating expenses often cannot be easily identified by when payments are received or made during the accounting periods that they affect. What a company expects to pay during a particular accounting period is included in an expense account while what it pays during the period goes into a prepaid expense account. There is no fixed approach to identifying the period expense in all the particulars. The Management accountant has to carefully evaluate the time cost and check whether the same will form part of an income statement.
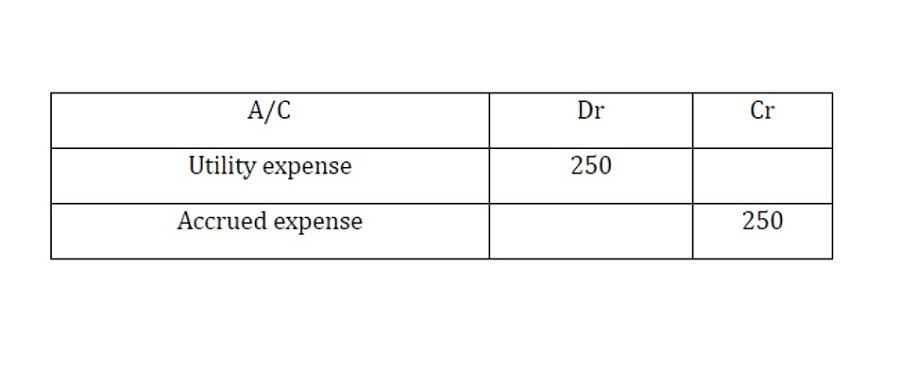
However, if these costs become excessive they can add significantly to total expenses and they should be monitored closely so managers can take action to reduce them when possible. Examples include production materials consumed in making a product and commissions paid to salespeople. What is paid during that period was $100,000 in rent and utilities, but only $10,000 in insurance and property taxes because a storm damaged the roof of one of its properties. It will keep accruing, and an entity will have to bear the same without profit or revenue. The person creating the production cost calculation, therefore, has to decide whether these costs are already accounted for or if they must be a part of the overall calculation of production costs. Period costs are of no less help, as they allow you to understand how well you’re running your business.
- These costs are identified as being either direct materials, direct labor, or factory overheads, and they are traceable or assignable to products.
- This forward-looking approach enables companies to predict potential financial challenges and opportunities, allowing for proactive adjustments to their strategies.
- On the other hand, if a cost is linked to a product, inventory, production, or goods and may be incurred over several accounting periods, you may be looking at a product cost.
- Period expenses are costs that help a business or other entity generate revenue, but aren’t part of the cost of goods sold.
- This necessitates a thorough analysis of both direct and indirect expenses to determine the minimum price at which a product can be sold without incurring a loss.
- Imagine your favorite bakery – the cost of flour, sugar, and the baker’s time to make those croissants you’re so fond of.
- The fixed cost per unit of output will vary inversely with changes in output level.
- They play a significant role in shaping the overall profitability of a business because they directly impact how much money it gets to keep after covering all these ongoing expenses.
- The product costs are sometime named as inventoriable costs because they are initially assigned to inventory and expensed only when the inventory is sold and revenue flows into the business.
- Production costs are usually part of the variable costs of business because the amount spent will vary in proportion to the amount produced.
- Out of these 500 units manufactured, the company sells only 300 units during the year 2022 and 200 unsold units remain in ending inventory.
- They are referred to as period costs because they are not assigned to products, and therefore cannot be included in the cost of items held in inventory.
- For example, a company will deduct expenses such as sales costs, overhead costs, rent, or marketing expenses from its total income to derive its net income.
Period expenses are usually calculated by adding together all expected payments for a period, then subtracting any amounts that were paid early. Time cost forms a significant portion of indirect costs, hence critical for running the business. Discover the key to effective financial management with our straightforward guide on variance reporting. For the past 52 years, Harold Averkamp (CPA, MBA) hasworked as an accounting supervisor, manager, consultant, university instructor, and innovator in teaching accounting online. For the past 52 years, Harold Averkamp (CPA, MBA) has worked as an accounting supervisor, manager, consultant, university instructor, and innovator in teaching accounting online. A financial professional will offer guidance based on the information provided and offer a no-obligation call to better understand your situation.
Related AccountingTools Course

To make a profit and keep your bakery thriving, you’ll likely set a price for your cakes that’s higher than $10. Product costs help you set these prices, ensuring you cover all the expenses and have some left for profit. So, product costs become your pricing compass, guiding you to set prices that keep your bakery in business. In a manufacturing organization, an important distinction exists between product costs and period costs. In a manufacturing organization, an important difference exists between product costs and period costs.
